1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Simhei']
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
x_data= [ 338., 333., 328., 207., 226., 25., 179., 60., 208., 606.]
y_data= [ 640., 633., 619., 393., 428., 27., 193., 66., 226., 1591.]
x = np.arange(-200, -100, 1)
y = np.arange(-5,5,0.1)
Z = np.zeros((len(x), len(y)))
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
for i in range(len(x)):
for j in range(len(y)):
b = x[i]
w = y[j]
Z[j][i] = 0
for n in range(len(x_data)):
Z[j][i] = Z[j][i] + (y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n]) **2
Z[j][i] = Z[j][i] /len(x_data)
b = -120
w = -4
lr =0.0000001
iteration = 100000
b_history = [b]
w_history = [w]
for i in range(iteration):
b_grad = 0.0
w_grad = 0.0
for n in range(len(x_data)):
b_grad = b_grad - 2.0*(y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n]) *1.0
w_grad = w_grad - 2.0*(y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])*x_data[n]
b = b - lr * b_grad
w = w - lr * w_grad
b_history.append(b)
w_history.append(w)
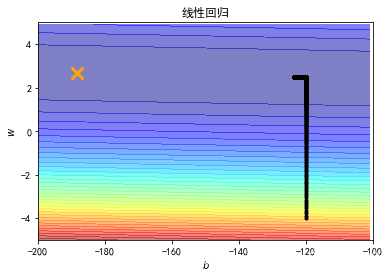
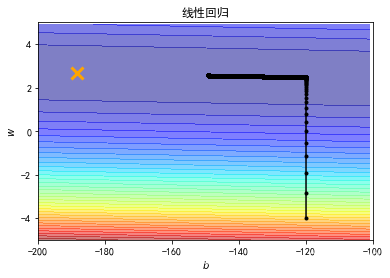
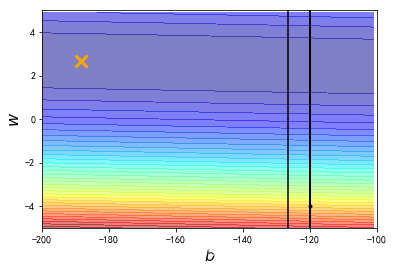
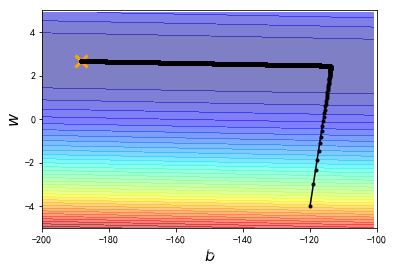
plt.contourf(x, y, Z, 50, alpha = 0.5, cmap=plt.get_cmap('jet'))
plt.plot([-188.4], [2.67], 'x', ms = 12, markeredgewidth = 3, color='orange')
plt.plot(b_history, w_history, 'o-', ms=3, lw=1.5, color='black')
plt.xlim(-200, -100)
plt.ylim(-5,5)
plt.xlabel(r'$b$', fontsize=16)
plt.ylabel(r'$w$', fontsize=16)
plt.title("线性回归")
plt.show()
|